The 1.5°C limit
Share
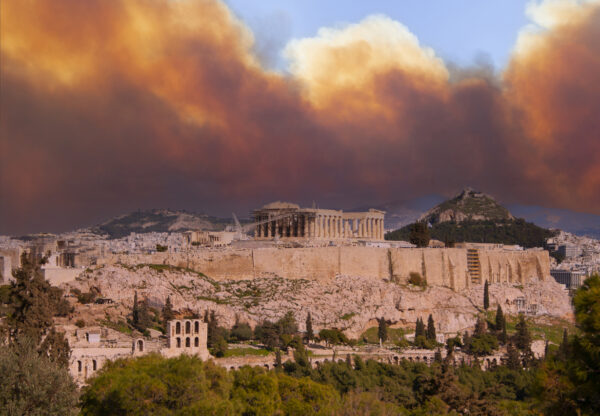
The 1.5°C warming limit is the cornerstone of ambitious climate action. The science tells us keeping within this limit is feasible and is essential if we are to avoid permanent and devastating climate impacts.
We have pioneered science detailing the impacts of warming at 1.5°C compared to higher levels of warming to illustrate the relevance and urgency of climate action. Our policy analysis and advice is also framed around this limit to set out what climate action in line with the best science looks like from national to global levels.

Is the 1.5°C limit still in reach?

Understanding the Paris Agreement’s Long Term Temperature Goal
Our experts

Bill Hare(D.Sc. (hon. causa) (Murdoch))
CEO / Senior Scientist

Dr Fahad Saeed
Senior Climate Scientist

Prof Dr Michiel Schaeffer
Chief Scientist, Co-founder

Uta Klönne
Senior Science Advisor
Publications
Projects

Climate Action Tracker
The Climate Action Tracker is an independent science-based assessment, which tracks the emission commitments and actions of countries.

Climate ambition support
Supporting climate-vulnerable countries in strengthening their roles and voices in international climate negotiations.

1.5°C national pathways
The 1.5°C national pathway explorer, developed in collaboration with the IKEA Foundation, uses global and regional IPCC models to develop national and sectoral decarbonisation pathways.

Climate and Earth system responses to climate neutrality and net negative emissions
The RESCUE (Response of the Earth System to overshoot, Climate neutrality and negative Emissions) project aims to improve our knowledge and understanding of the climate and Earth system responses to climate neutrality and net negative emissions.

Coal phase-out
Coal is the most carbon intensive fossil fuel - phasing it out is key to achieving the 1.5°C Paris Agreement goal. Most emissions from coal are in the electricity sector, so coal’s phase-out is relatively cheap and easy, as the technologies that can replace it already exist. Our research shows coal needs to be phased out globally by 2040 for the world to meet its climate commitments.

Understanding the climate impacts associated with temporarily overshooting 1.5°C
This project is working to develop the science around what the climate impacts of temporarily overshooting 1.5°C would mean for our climate.

Analysing issues of fairness for carbon dioxide removal
The Carbon Dioxide Removal Options: Policies and Ethics (CDR-PoEt) project examines policy instruments and pathways towards fair deployment of carbon dioxide removal to meet the objectives of the Paris Agreement.

Assessment of mitigation pathways and cost estimates
The Assessment of climate change Mitigation Pathways and Evaluation of the Robustness of mitigation cost Estimates (AMPERE) project makes multi-model comparisons to better understand climate and cost uncertainties.

Climate change risk analysis to support the Network for Greening the Financial System
The Network of Central Banks and Supervisors for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) is a voluntary group of banks and supervisors that aim to share best practices on climate risk management in the financial sector and to mobilise mainstream finance to promote the transition to a sustainable economy. Climate Analytics contributes to this work by providing estimates of risk from climate change impacts using future climate projections and makes them publicly available through the Climate Impact Explorer online tool.

IMPACT

Climate mitigation potential for European forests and forest-based sectors

Climate risk, adaptation and insurance in the Caribbean
The Climate Risk Adaptation and Insurance in the Caribbean (CRAIC) project, led by Munich Climate Insurance Initiative, assists Caribbean countries in their efforts to increase social resilience and adapt to climate change by incorporating climate risk insurance within a broader framework of disaster risk reduction strategies.

Land management strategies to mitigate and adapt to climate change
The project aims to investigate how changes in land cover and land management can help to meet the mitigation and adaptation objectives of the Paris Agreement, and the Sustainable Development Goals.

Assessing the differences in climate impacts between 1.5°C and 2°C

Turn down the heat report series
From 2012 to 2014 we authored a series of reports for the World Bank looking at the impacts of climate change in a 4°C world with an emphasis on the impacts for the most vulnerable.

High-Level support for LDCs and SIDS on climate change
The HLSM High-Level Support Mechanism for LDC and SIDS on Climate Change project creates a support mechanism for high-level political representatives and their advisors from LDCs and SIDS that is demand-driven, responsive to ongoing needs and firmly rooted in the respective regions.

SURVIVE
SURVIVE, a joint project between Climate Analytics and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) supports Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and Least Developed Countries (LDCs) in the international climate change negotiations.

PREVENT
PREVENT is built around a team of experienced climate scientists and analysts, whose objective is to provide science, policy, strategic and analytical support for delegations of the Least Developed Countries and Small Island Developing States.

Support for preparing Intended Nationally Determined Contributions
We assisted the Governments of a number of countries in their domestic preparation for the formulation of their intended nationally determined contributions (INDCs), in the context of the 2015 climate agreement.